Difference between revisions of "Crashplan"
(→Linux) |
|||
| Line 121: | Line 121: | ||
Starting on your X desktop (Gnome, KDE, ...), open a Terminal (Applications >System > Terminal in Fedora)<br/> | Starting on your X desktop (Gnome, KDE, ...), open a Terminal (Applications >System > Terminal in Fedora)<br/> | ||
and enter the following commands: | and enter the following commands: | ||
| + | {{Code|ssh -X hda}} | ||
| − | + | Follow the commands above for the specific OS you are running on your HDA. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Once you're done with the CrashPlan configuration, you can close the CrashPlan app, and the Terminal. | Once you're done with the CrashPlan configuration, you can close the CrashPlan app, and the Terminal. | ||
Revision as of 20:46, 12 July 2012
Contents
CrashPlan on Amahi
Using CrashPlan on your Amahi HDA will allow you to back up, for free1, all your computers into your Amahi HDA2.
It will also allow you to become the backup server of friends and family, if you'd like.
1 While CrashPlan is free to personal use, an advanced version, CrashPlan+, is available for a fee, if you'd like to get the features it adds to the free CrashPlan version.
2 Technically, it's also possible to backup your HDA into your other computers if you need that.
Installing CrashPlan
To be able to use CrashPlan, you'll need to install the CrashPlan application on your Amahi HDA, configure it as needed, and install the CrashPlan application on all the computers you'd like to backup to your HDA.
More about CrashPlan
To learn more about CrashPlan, you can visit the CrashPlan website, where features are explained, and where you can watch CrashPlan in action in their video tour.
CrashPlan Accounts
Using CrashPlan requires a (free) CrashPlan account. You'll be able to create a new account from the configuration app itself.
You'll probably want to use the same account for all computers in your home. That means you'll create the account on the first computer you configure CrashPlan on (it can be your HDA, or any other computer on your home network), and then simply use that same account on all other computers, instead of creating new accounts.
If you'd like to use different accounts, so that each computer (user) is the sole owner of his backed up files, this is also possible. Trying to restore such files from another computer (this is called a guest restore in CrashPlan) will require the user to enter the owner's password.
How to configure CrashPlan on your HDA
NOTE The CrashPlan UI sometimes has issues registering button clicks. If you click a button and it seems to do nothing, hit the ENTER key. That seems to help in such cases.
On the HDA itself
The easiest way to configure CrashPlan is to access it from the HDA desktop directly.
Launch a Terminal (Applications > System > Terminal).
In the terminal window (must run as root user) enter:
Fedora:
| bash code |
|---|
su - CrashPlanDesktop
|
Ubuntu:
| bash code |
|---|
sudo CrashPlanDesktop
|
If you don't have physical access to your HDA, or if you run it headless, try the methods below.
Using VNC
If you have VNC or WebVNC setup, you can use that to configure CrashPlan remotely, instead of using the OS-dependent methods described below.
Simply connect to your HDA using VNC (or WebVNC), and launch a Terminal (Applications > System > Terminal).
In the terminal window follow the same steps above.
The CrashPlan configuration application will start.
Using X-Forwarding
To use X-Forwarding, you don't need X running, or even installed on your HDA.
All you need is an X server on your client computer, and to SSH into your HDA with X-Forwarding enabled.
Windows
PuTTY and Xming
You'll need two things to be able to configure CrashPlan from Windows: PuTTY and Xming.
For PuTTY, just download putty.exe from here. You can leave it on your desktop and use it from there.
For Xming, you'll need to download and install two files: the Xming installer, and the fonts installer.
You can accept all the default values for both installs.
Now, you should have a start menu item for Xming. Start it from there. You should now have a black X icon in your system tray.
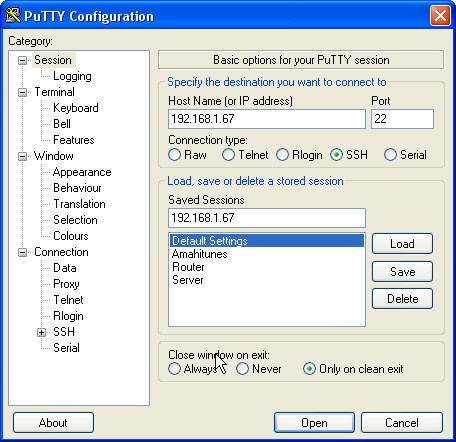
Next, start PuTTY, and enter your HDA IP address under Host Name (or IP address), enter 22 under Port and select SSH under Connection Type.
Open the Connection > SSH item in the Category tree on the left, and select X11.
Select the checkbox that says Enable X11 forwarding.
Now go back into Session in the Category tree, and give a name for this profile, so you won't have to repeat those steps next time.
Enter a name in the Saved Sessions text box, and hit the Save button on the right.
Next time your start PuTTY, you'll be able to just double-click your profile in the Saved Sessions section to connect to your HDA with X11 forwarding enabled.
Now, connect to your HDA by clicking Open, or double-clicking your profile name in the Saved Sessions select box (on the left of the Load, Save and Delete buttons).
Enter your Fedora username and password when prompted.
FreeXer
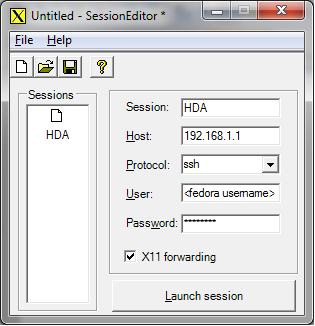
FreeXer is an open source attempt to make X11 forwarding easy. It consists of PuTTY and Cygwin with a wrapper that configures both to enable X11 forwarding.
First, download FreeXer here.
Once installed, open the "freeXer Session Editor" and enter a name for the session you're about to start under Session, enter your HDA IP address under Host, select SSH under Protocol, enter your Fedora username under User and password under Password.
Click on the Save button to save the session information. Once you saved the session information, the next time you need it you only need to open the session information file (or load it into the session editor) and you're done.
When ready, click on the Launch Session button.
Once logged in
Enter the following command to start the CrashPlan configuration UI:
Enter the same commands as above depending on the OS.
Guides
There are many guides available online that explain the steps of X11 forwarding. Here's some, if you need further help:
- X Windows Forwarding video on YouTube
- Using X Forwarding on Windows at Caltech
- X Forwarding with Putty on Windows at University of Minnesota
Mac OS X
Open a Terminal (Applications > Utilities > Terminal.app)
and enter the following commands:
| bash code |
|---|
ssh -X hda
|
Then enter the same commands as outlined above for the OS you are running on the HDA.
Once you're done with the CrashPlan configuration, you can close the CrashPlan app, the X11.app that appeared in your Dock, and Terminal.app
Linux
Starting on your X desktop (Gnome, KDE, ...), open a Terminal (Applications >System > Terminal in Fedora)
and enter the following commands:
| bash code |
|---|
ssh -X hda
|
Follow the commands above for the specific OS you are running on your HDA.
Once you're done with the CrashPlan configuration, you can close the CrashPlan app, and the Terminal.
Using a local CrashPlan client
You can follow the instructions on the CrashPlan wiki on how to connect to a headless CrashPlan install.
It requires you to install CrashPlan on your client computer, manually editing a config file, and using SSH port forwarding.
Troubleshooting
If you have problems running the Desktop UI on the local machine for the first time, enter this command in the terminal:
sudo chmod 666 /usr/local/crashplan/log/*.log
Then try re-running CrashPlanDesktop