Difference between revisions of "TigerVNC"
From Amahi Wiki
m |
|||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
yum install tigervnc-server | yum install tigervnc-server | ||
| − | *Once install create | + | *The following example is if you wish to setup access under root control, if you wish to setup under normal user the see below under Multiply User Setup |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *Once install we need to create new configuration file, vncserver@.service is only a template file, from this we need t create a the following config file. | ||
cp /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@.service /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@:1.service | cp /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@.service /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@:1.service | ||
| Line 180: | Line 184: | ||
systemctl disable vncserver@:1.service | systemctl disable vncserver@:1.service | ||
systemctl stop vncserver@:1.service | systemctl stop vncserver@:1.service | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | = Multiple User Setup = | ||
| + | |||
| + | * It is possible to setup multiple user login's other than root. For this example with will create 2 other users, Tom & Dick. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * First we need to create these user, either using the Amahi Dashboard under the USER setting or by the following commands under root control. | ||
| + | |||
| + | adduser <user name> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * For the example the commands will be | ||
| + | |||
| + | adduser tom | ||
| + | adduser dick | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Then create a password for that user using the following command | ||
| + | |||
| + | passwd <user name> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * For this example the command will be | ||
| + | |||
| + | passwd tom | ||
| + | passwd dick | ||
| + | |||
| + | * When requested enter a password and renter the password to verify it for each user created. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Once the user are created we will need to assign configuration files for each user. For this will assign the following config files as followed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Tom will be assigned the following config file using the following. | ||
| + | |||
| + | cp /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@.service /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@:2.service | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Dick will be assigned the following config file. | ||
| + | |||
| + | cp /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@.service /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@:3.service | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Once the config files are created we will need to modify them for the correct user access. Accessing the files using your favourite editor the config files need to be modified under [Service] to reflect the assigned user. For this example the files should look like the following. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * For Tom (under root control) | ||
| + | |||
| + | nano /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@:2.service | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Then modify the [Service] as followed | ||
| + | |||
| + | [Service] | ||
| + | Type=forking | ||
| + | # Clean any existing files in /tmp/.X11-unix environment | ||
| + | ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :' | ||
| + | ExecStart=/sbin/runuser -l tom -c "/usr/bin/vncserver %i" | ||
| + | PIDFile=/home/tom/.vnc/%H%i.pid | ||
| + | ExecStop=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :' | ||
| + | |||
| + | * For Dick (under root control) | ||
| + | |||
| + | nano /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@:3.service | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Then modify the [Service] as followed | ||
| + | |||
| + | [Service] | ||
| + | Type=forking | ||
| + | # Clean any existing files in /tmp/.X11-unix environment | ||
| + | ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :' | ||
| + | ExecStart=/sbin/runuser -l dick -c "/usr/bin/vncserver %i" | ||
| + | PIDFile=/home/dick/.vnc/%H%i.pid | ||
| + | ExecStop=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :' | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Once the config files are created we need to assign password to access vnc-server for each user, for this each user need to login in via terminal and | ||
| + | run the the command as above under the password section | ||
| + | |||
| + | vncpasswd | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Once each user has created a password, then each user needs to login in under terminal and modify the xstarup file to reflect the chosen desktop environment as listed above. Each user can access the file as followed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | cd ~/.vnc | ||
| + | nano xstartup | ||
| + | |||
| + | * For this example we will use the MATE-Desktop Environment, each user will copy the following into their xstartup file. | ||
| + | |||
| + | #!/bin/sh | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | # Uncomment the following two lines for normal desktop: | ||
| + | # unset SESSION_MANAGER | ||
| + | unset DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS | ||
| + | # exec /etc/X11/xinit/xinitrc | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | [ -x /etc/vnc/xstartup ] && exec /etc/vnc/xstartup | ||
| + | [ -r $HOME/.Xresources ] && xrdb $HOME/.Xresources | ||
| + | xsetroot -solid grey | ||
| + | vncconfig -iconic & | ||
| + | x-terminal-emulator -geometry 80x24+10+10 -ls -title "$VNCDESKTOP Desktop" & | ||
| + | mate-session & | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Once each xstartup file is modified we need to start each service. Login as root and run the following commands. | ||
| + | |||
| + | systemctl enable vncserver@:2.service | ||
| + | systemctl enable vncserver@:3.service | ||
| + | systemctl start vncserver@:2.service | ||
| + | systemctl start vncserver@:3.service | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Once the services are running then each user can access their remote desktop using a client software as listed below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * From the example tom's access ip address will be | ||
| + | |||
| + | 192.168.1.10:2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * For dick's the access ip address will be | ||
| + | |||
| + | 192.168.1.10:3 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
= Windows Client Software = | = Windows Client Software = | ||
Revision as of 12:03, 1 January 2014

|
Work In Progress |
|---|---|
| This article is currently undergoing major expansion or restructuring. You are welcome to assist by editing it as well. If this article has not been edited in several days, please remove this template. |
| WARNING | |
|---|---|
| This should only be attempted by advanced users. It is still under development. |
Contents
Amahi 7 (Fedora 19) Desktop Installation
For TigerVNC to work an Desktop Environment must be installed even if the HDA does not boot to the selected Desktop Environment. So far KDE and Mate Desktop Environments have been tested.
MATE-Desktop Environment
- As root, install MATE-Desktop Environment:
yum groupinstall mate-desktop-extra
KDE-Desktop Environment
- As root, install KDE-Desktop Environment:
yum install @kde-desktop
TigerVNC Server Installation
- It is recommended to only use TigerVNC on a secure network or via a VPN.
- As root, install the server:
yum install tigervnc-server
- The following example is if you wish to setup access under root control, if you wish to setup under normal user the see below under Multiply User Setup
- Once install we need to create new configuration file, vncserver@.service is only a template file, from this we need t create a the following config file.
cp /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@.service /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@:1.service
- Open the new configuration file
nano /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@:1.service
- The configuration will look like this
# The vncserver service unit file
#
# Quick HowTo:
# 1. Copy this file to /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@:<display>.service
# 2. Edit <USER> and vncserver parameters appropriately
# ("runuser -l <USER> -c /usr/bin/vncserver %i -arg1 -arg2")
# 3. Run `systemctl daemon-reload`
# 4. Run `systemctl enable vncserver@:<display>.service`
#
# DO NOT RUN THIS SERVICE if your local area network is
# untrusted! For a secure way of using VNC, you should
# limit connections to the local host and then tunnel from
# the machine you want to view VNC on (host A) to the machine
# whose VNC output you want to view (host B)
#
# [user@hostA ~]$ ssh -v -C -L 590N:localhost:590M hostB
#
# this will open a connection on port 590N of your hostA to hostB's port 590M
# (in fact, it ssh-connects to hostB and then connects to localhost (on hostB).
# See the ssh man page for details on port forwarding)
#
# You can then point a VNC client on hostA at vncdisplay N of localhost and with
# the help of ssh, you end up seeing what hostB makes available on port 590M
#
# Use "-nolisten tcp" to prevent X connections to your VNC server via TCP.
#
# Use "-localhost" to prevent remote VNC clients connecting except when
# doing so through a secure tunnel. See the "-via" option in the
# `man vncviewer' manual page.
[Unit]
Description=Remote desktop service (VNC)
After=syslog.target network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
# Clean any existing files in /tmp/.X11-unix environment
ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'
ExecStart=/sbin/runuser -l <USER> -c "/usr/bin/vncserver %i"
PIDFile=/home/<USER>/.vnc/%H%i.pid
ExecStop=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
- Under [Service] replace with the following. Please note this is for root access ONLY, see below on how to setup for other users.
[Service]
Type=forking
User=root
# Clean any existing files in /tmp/.X11-unix environment
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i
ExecStart=/usr/bin/vncserver %i
ExecStop=/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i
Setup Desktop Environment Access
- Modification of the ~/.vnc/xstartup will be required to match the chosen Desktop-Environment
- As root create a backup of the existing xstartup file
cd ~/.vnc
mv xstartup xstartup.bak
nano xstartup
MATE-Desktop Environment
- As root, remove the context of the xstartup file and replace with the following.
#!/bin/sh
#
# Uncomment the following two lines for normal desktop:
# unset SESSION_MANAGER
unset DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS
# exec /etc/X11/xinit/xinitrc
#
[ -x /etc/vnc/xstartup ] && exec /etc/vnc/xstartup
[ -r $HOME/.Xresources ] && xrdb $HOME/.Xresources
xsetroot -solid grey
vncconfig -iconic &
x-terminal-emulator -geometry 80x24+10+10 -ls -title "$VNCDESKTOP Desktop" &
mate-session &
- Once file has been modified run the following command
systemctl daemon-reload
KDE-Desktop Environment
- As root, remove the context of the xstartup file and replace with the following.
#!/bin/sh
#
# Uncomment the following two lines for normal desktop:
#unset SESSION_MANAGER
#exec /etc/X11/xinit/xinitrc
#
[ -x /etc/vnc/xstartup ] && exec /etc/vnc/xstartup
[ -r $HOME/.Xresources ] && xrdb $HOME/.Xresources
#xsetroot -solid grey
#vncconfig -iconic &
#xterm -geometry 80x24+10+10 -ls -title "$VNCDESKTOP Desktop" &
#twm &
startkde &
- Once file has been modified run the following command
systemctl daemon-reload
Password Setup
- Set the VNC password for the user as defined in the vncserver@:1.service
- From the example log into terminal as root and run the following command
vncpasswd
- The following response will appear waiting for a password to be entered
Password:
- The following response will appear waiting to verify the password entered.
Verify:
Starting/Stopping TigerVNC Server
- The following commands will allow you to autostart and start the service.
systemctl enable vncserver@:1.service
systemctl start vncserver@:1.service
- The following commands will allow you to disable autostart and stop the service.
systemctl disable vncserver@:1.service
systemctl stop vncserver@:1.service
Multiple User Setup
- It is possible to setup multiple user login's other than root. For this example with will create 2 other users, Tom & Dick.
- First we need to create these user, either using the Amahi Dashboard under the USER setting or by the following commands under root control.
adduser <user name>
- For the example the commands will be
adduser tom adduser dick
- Then create a password for that user using the following command
passwd <user name>
- For this example the command will be
passwd tom passwd dick
- When requested enter a password and renter the password to verify it for each user created.
- Once the user are created we will need to assign configuration files for each user. For this will assign the following config files as followed.
- Tom will be assigned the following config file using the following.
cp /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@.service /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@:2.service
- Dick will be assigned the following config file.
cp /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@.service /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@:3.service
- Once the config files are created we will need to modify them for the correct user access. Accessing the files using your favourite editor the config files need to be modified under [Service] to reflect the assigned user. For this example the files should look like the following.
- For Tom (under root control)
nano /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@:2.service
- Then modify the [Service] as followed
[Service] Type=forking # Clean any existing files in /tmp/.X11-unix environment ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :' ExecStart=/sbin/runuser -l tom -c "/usr/bin/vncserver %i" PIDFile=/home/tom/.vnc/%H%i.pid ExecStop=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'
- For Dick (under root control)
nano /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@:3.service
- Then modify the [Service] as followed
[Service] Type=forking # Clean any existing files in /tmp/.X11-unix environment ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :' ExecStart=/sbin/runuser -l dick -c "/usr/bin/vncserver %i" PIDFile=/home/dick/.vnc/%H%i.pid ExecStop=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'
- Once the config files are created we need to assign password to access vnc-server for each user, for this each user need to login in via terminal and
run the the command as above under the password section
vncpasswd
- Once each user has created a password, then each user needs to login in under terminal and modify the xstarup file to reflect the chosen desktop environment as listed above. Each user can access the file as followed.
cd ~/.vnc nano xstartup
- For this example we will use the MATE-Desktop Environment, each user will copy the following into their xstartup file.
#!/bin/sh
#
# Uncomment the following two lines for normal desktop:
# unset SESSION_MANAGER
unset DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS
# exec /etc/X11/xinit/xinitrc
#
[ -x /etc/vnc/xstartup ] && exec /etc/vnc/xstartup
[ -r $HOME/.Xresources ] && xrdb $HOME/.Xresources
xsetroot -solid grey
vncconfig -iconic &
x-terminal-emulator -geometry 80x24+10+10 -ls -title "$VNCDESKTOP Desktop" &
mate-session &
- Once each xstartup file is modified we need to start each service. Login as root and run the following commands.
systemctl enable vncserver@:2.service systemctl enable vncserver@:3.service systemctl start vncserver@:2.service systemctl start vncserver@:3.service
- Once the services are running then each user can access their remote desktop using a client software as listed below.
- From the example tom's access ip address will be
192.168.1.10:2
- For dick's the access ip address will be
192.168.1.10:3
Windows Client Software
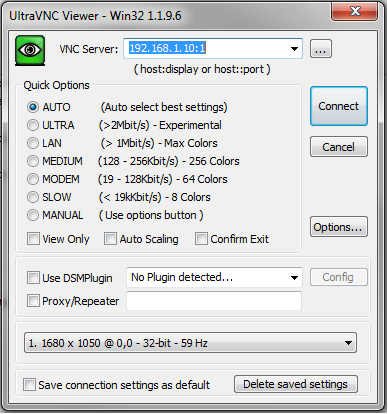
Download the latest Windows Client Software
Using UltraVNC for this example enter in the VNC Server text Box your hda ip address location with :1 as per the example picture below
The :1 refers to the vncserver@:1.service file that was modified
If connection is successful it will as for a password, which is the password entered from the setup above.
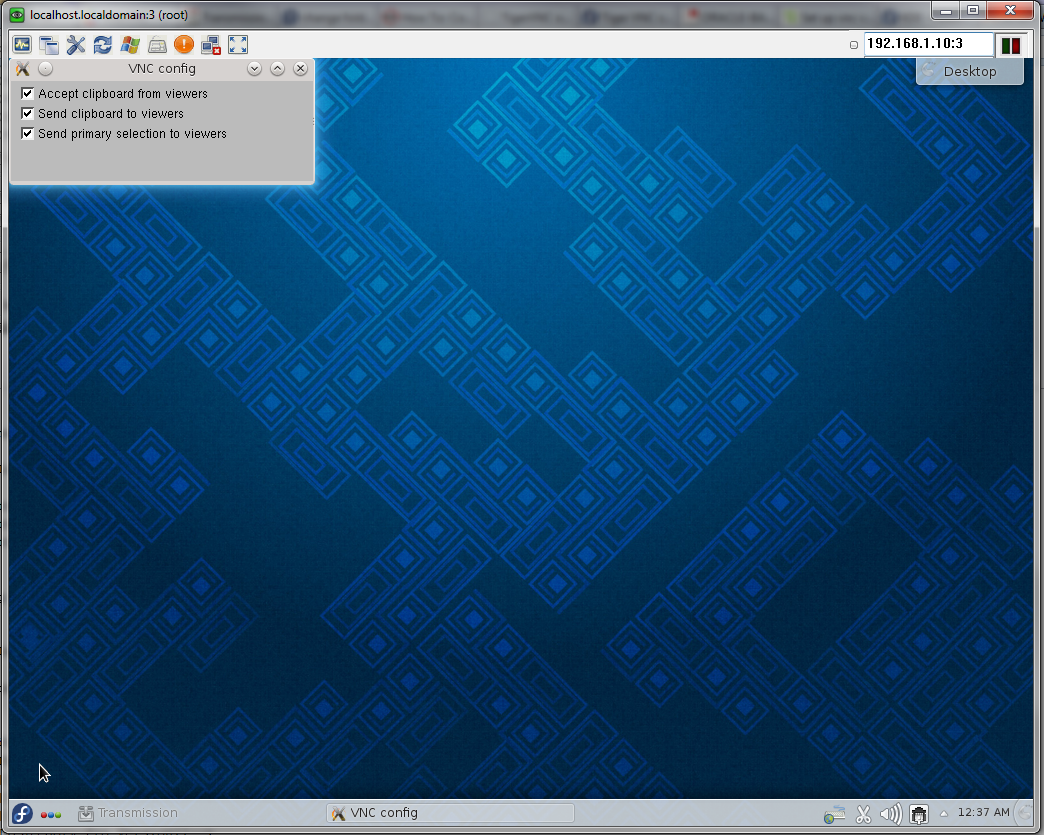
Screenshots
Screenshot of KDE Remote Desktop