Hosting a website
NOTICE: making anything visible outside your network can open security issues, so you are doing this at your own risk. Some apps are more secure than others, but there is nothing ultimately secure. Best is to use the VPN to login back home.
To access the HDA itself from outside the network using VPN, check out the OpenVPN ALS application, available to install through the HDA. It enables you to access the HDA, and all applications and folders, using just your free username.yourhda.com webaddress.
So you want to run a web server in your Amahi server and make it visible from the web outside your home.
Contents
Requirements
For the purposes of this guide you need either of the following:
- VNC access to your HDA if headless
- Terminal is available under Applications -> System Tools -> Terminal
- Ajaxterm if headless and no VNC
- A monitor if you are not headless
To host your own web site you need the following:
- Forward a port to your HDA ip address, either for plain insecure http: 80, for https, 443 (advanced users can use other ports). Some routers call this or require a "virtual server"
- Chose a domain name that you own (or your free username.yourhda.com that comes with Amahi). This is how the app will be accessed outside
- Chose the app you want to make accessible outside, let's say, yourwebappname
Hosting a single Webapp
What you need to do in a terminal (as root) is find the apps conf file then edit the conf file for the app:
| bash code |
|---|
su [enter password] ls /etc/httpd/conf.d
|
Find your app .conf file. It will look like 10##-yourwebappname.conf
| bash code |
|---|
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/10##-yourwebappname.conf
|
Your conf file should look something like this at the top of the page:
| Text |
|---|
<VirtualHost *:80> ServerName app ServerAlias app.YourDomain.lan </VirtualHost>
|
Add this (immediately after the ServerName directive):
| Text |
|---|
ServerAlias username.yourhda.com
|
So it looks like this:
| Text |
|---|
<VirtualHost *:80> ServerName app ServerAlias app.YourDomain.lan ServerAlias username.yourhda.com </VirtualHost>
|
You can add more server aliases if you want to access the app under those names (for example: ServerAlias myphotos.DomainName.com). Once you are satisfied with the server aliases, you may save and quit nano by following these steps in Windows:
ctrl X
At the prompt, type "y" to save
At the prompt, hit "Enter" to save the file
Restart the server using:
- Fedora
| bash code |
|---|
service httpd reload
|
- Ubuntu
| bash code |
|---|
sudo service apache2 reload
|
And you are done, enjoy your website.
Hosting Multiple Webapps
If you wish to have access to multiple webapps, described below is one way to accomplish this:
- obtain a domain name (i.e., via godaddy.com) --for example yourdomain.com
- for each web app you wish to have access to, establish a CNAME or subdomain--for example something.yourdomain.com---and point it to username.yourhda.com (for example see http://help.godaddy.com/article/679 )
- edit the webapp .conf file (see above) to match the CNAME/subdomain you just established by adding ServerAlias something.yourdomain.com
- don't forget to restart the server each time you edit a .conf file.
- For example, you could create the subdomain/CNAME: address.yourdomain.com for the AddressBook webapp---point that subdomain to: username.yourhda.com---in the AddressBook .conf file add: ServerAlias address.yourdomain.com---restart the server---you are done, enjoy using multiple webapps!
Even if you have a dynamic IP address from your ISP, this can still be done - rather inexpensively. Some dynamic DNS services, like DynDNS, allow for you to create a domain and use something called a wildcard DNS record. This acts much like the subdomain created above, but you can literally use anything you want so long as the server is set to answer to the request. Below, we'll outline the basic steps needed to accomplish this.
Some routers (Netgear, Linksys, etc.) allow you to set up credentials for your dynamic DNS service account so that it'll update the dynamic DNS service for you. If you don't have that ability, you may have to run a client-side application on a computer inside your network which will send out regular updates to do the same thing. Figure out if you will be updating the dynamic DNS service via the router or a client-side app. Once you've confirmed you can utilize this technology, in one form or another, proceed with the rest of these basic steps.
- Obtain a paid DynDNS account.
- At the time of this writing, DynDNS is calling it their Pro account.
- Basic accounts will not allow you to use wildcards.
- In your Amahi's web-GUI, navigate to your Webapps section via Apps > Webapps.
- In our case, we'll be allowing our Dokuwiki to answer to our wildcard DNS record so expand it by clicking on it.
- This will show several options to edit but we're only going to add an alias.
- Click on New Alias.
- Enter your wildcard like what we have in our example.
- If your DynDNS account is tommy.homedns.org, you'll enter something like wiki.tommy.homedns.org. Again, DynDNS allows for wildcards so you can make up stuff all day long!
- This will show several options to edit but we're only going to add an alias.
You should be able to test this by now however, it may prove difficult to accurately test it from inside your own network. In that case, bug your friend down the street to see if they can get to it or do it yourself at a later date.
For the curious: So, what did this do? Well, what it did was add a ServerAlias directive to the Apache configuration. (In MS-IIS, it's called a host header or a binding.) You can have as many ServerAlias' as you'd like. So, if you wanted to take a look under the hood, you would open a terminal window on your server (or SSH to it) and do a directory listing of /etc/httpd/conf.d/.
| bash code |
|---|
user@ubuntu-amahi1:~$ ls -l /etc/httpd/conf.d/ total 28 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 21 Oct 10 18:46 00-init.conf -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2231 Oct 10 18:46 01-platform.conf -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 516 Oct 10 18:46 03-calendar.conf -rw-rw-r-- 1 nobody nogroup 518 Feb 1 09:20 1000-dokuwiki.conf -rw-rw-r-- 1 www-data users 492 Oct 10 21:14 1001-phpsysinfo.conf -rw-rw-r-- 1 www-data users 489 Oct 10 21:18 1002-subsonic.conf user@ubuntu-amahi1:~$
|
In our case, when we installed the Dokuwiki app, it created 1000-dokuwiki.conf. Open that and you'll see the ServerAlias that was added.
| bash code |
|---|
user@ubuntu-amahi1:~$ nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/1000-dokuwiki.conf <VirtualHost *:80> ServerName dokuwiki ServerAlias dokuwiki.home.local ServerAlias wiki.tommy.homedns.org DocumentRoot /var/hda/web-apps/dokuwiki/html <Directory "/var/hda/web-apps/dokuwiki/html"> Options Indexes FollowSymLinks +ExecCGI AddHandler fcgid-script .fcg AllowOverride FileInfo Limit Options Indexes Order allow,deny Allow from all </Directory> ErrorLog /var/hda/web-apps/dokuwiki/logs/error_log CustomLog /var/hda/web-apps/dokuwiki/logs/access_log combined env=!dontlog </VirtualHost>
|
You can see that adding that ServerAlias added the line: ServerAlias wiki.tommy.homedns.org
WARNING: Some apps will work right out of the box so to speak with these steps. Others however, (such as mediawiki) will require additional work before you can visit them on the internet. You will need to edit the apps config file to change the server address of that app. We will use mediawiki as an example.
So suppose I have a domain name, which is pointed at my hda - and I set up a subdomain that for the mediawiki app. We'll call it mediawiki.myname.com. After installing media wiki, I need to go
| bash code |
|---|
sudo vi /var/hda/web-apps/mediawiki/html/LocalSettings.php
|
And scroll down to
| bash code |
|---|
{{{1}}}
|
then change to
| bash code |
|---|
{{{1}}}
|
then enter these commands:
| bash code |
|---|
sudo rm -r /etc/lock/apache2 sudo php /var/hda/web-apps/mediawiki/html/maintenance/Update.php sudo service apache2 restart
|
Now you should be able to view http://mediawiki.myname.com from inside your network and on the internet as well.
Hosting a Website
Prerequisites: The first order of business is to make sure that your domain name is pointing to your server's IP address. Each website is different, but GoDaddy goes like this:
- Go to your GoDaddy's My Account page. Under Dashboard, click yourdomain.com
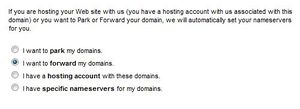
- Point your cursor at the Nameserver icon, click Set Nameservers
- Select I want to forward my domains and click OK
- Now go back to your account homepage, and instead of clicking yourdomain.com, check it and click View in Domain Manager
- Click yourdomain.com
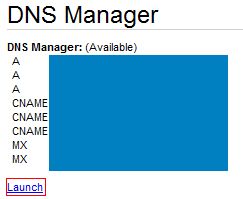
- Scroll down to DNS Manager and click Launch
- Under A(Host) edit the IP Address(es) to reflect the IP Address of your server. Hit enter and then Save Zone File when that option appears.
- The effects should appear within one hour
- Go to your GoDaddy's My Account page. Under Dashboard, click yourdomain.com
Hosting: Hosting a website on your HDA server is basically the same as hosting a webapp, so if we are able to do the previous guides on hosting a webapp(s) the rest will be a cinch.
We will create the website by creating a webapp. This is a lot easier than it sounds, so don't give up just yet!
- Got your HDA page (http://hda or http://hda.yourhda.com), click Setup and go to Settings.
- Make sure your Advanced Settings option is checked (if not, check and click OK past the warning)
- Go to Apps and then Webapps
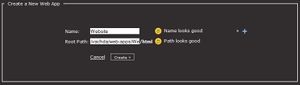
- At the very bottom, click New Web App and type in a name like Website
- This is where your webpage will reside in, you can name this anything you'd like. This is not the title of your website or webpage. Website will be used as the name for this guide
- Do everything as told under the "Hosting a single Webapp" heading above, but of course our app is called Website.
- Hint: Instead of using user.yourhda.com for your ServerAlias, go ahead and use yourdomain.com (without the www.) if you have one from, for example, GoDaddy.
- To easily access your website files, we will make the webapp folder a share by doing the following:
- In your HDA Dashboard, click Setup and then Shares
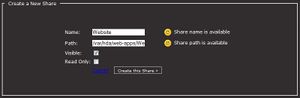
- Click New Share at the very bottom
- We will name our share Website
- Notice that the path is automatically filled out for us. This is not the path that will be used, so the path that will be typed in will be /var/hda/web-apps/Website/
- Click Create this Share, now the folder will be available from your normal \\hda spot.
- You can test your new website by creating an index.html (put something simple, like "hi", as a text) in the html folder in your Website share folder, and then going to yourdomain.com
And we are finished. To create your website on Fedora, we can use Bluefish program.
- yum install bluefish
If we would like to use Windows, we can use any program to make the website. Just drag and drop into the share, and under the folders as needed.
More Secure Access
To enable https access to your apps, you can follow the techniques in Secure App Access page.
FAQ
- Q: Do i need to do anything for
username.yourhda.comto work?
No. That comes free and automatically set up with your Amahi HDA
- Q: What if i want to do it for a .html or .php file?
You can do this by creating a Webapp of your own. In the apps tab,
select Webapps and create a new one.
What you do is, create a web app, and put the files into the root
directory of the webap, something like this directory:
/var/hda/web-apps/yourwebappname/html
this directory belongs to apache. you will have to change the
ownership to your user (recommended) or otherwise add things as root.
- Q: How do I change the ownership?
You can do this by going to the command screen:
su -
{password}
chown {user} /var/hda/web-apps/
Troubleshooting
- Q: When I go to myusername.yourhda.com I get my router's homepage instead of my hda. How do I fix that?
If you see your router's page, that means the forwarding did not take place from the external port to the internal port in your HDA
- Q: I do not see the app I want when accessing myusername.yourhda.com
This may be because the corresponding virtualhost does not have the name you expect on it, or because another virtualhost already has it and happens to take over