Adding a second hard drive to your HDA
| WARNING | |
|---|---|
| This is recommended only for Advanced users, proceed with caution. |
NOTE: In the future, Amahi Disk Wizard application (in Development) will provide this capability from the Dashboard.
The purpose of this tutorial is to make partitioning, formatting, and mounting hard drives in the Amahi server simple for those new to Linux.
The scenario is to have an HDA with a single hard drive, but want to connect additional hard drive(s) for increased storage. Examples provided are for adding a single hard drive.
In order to keep this process simple, it's important NOT to connect additional hard drive(s) until the end of the Preparation step.
Contents
Disclaimer
- Amahi cannot be held responsible for any data breakage or destruction arising from the use or misuse of this script. We provide it as a service in good will. You accept this automatically if you use the script.
- GUID-partitioned drives (such as drives previously in a Mac or have GPT partition tables) are not supported in this tutorial.
- nano is used as the command-line text editor (refer to beginners guide to nano as needed).
Prerequisites
In a Terminal, as root, verify disk tools are installed by executing:
Fedora
yum -y install pmount fuse fuse-libs ntfs-3g util-linux-ng parted nano
Ubuntu
sudo apt-get -y install gparted
- NOTE: Drives must be formatted as MBR not GUID/GPT for hda-diskmount to recognize the disk.
Preparation
In terminal as root, execute the following to capture current hard drive configuration:
ls -l /dev/disk/by-id/ > before.txt cat before.txt
- EXAMPLE:
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 2010-02-18 03:24 ata-Hitachi_HDS722020ALA330_JK1131YAGDU37V -> ../../sda lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 2010-02-18 03:24 ata-Hitachi_HDS722020ALA330_JK1131YAGDU37V-part1 -> ../../sda1
Power OFF the HDA and install/connect any additional hard drive(s).
Identify
Power ON the HDA and collect data about the new hard drive configuration. Again, save this to a text file for reference.
In a terminal as root, execute the following to capture current hard drive configuration:
ls -l /dev/disk/by-id/ > after.txt cat after.txt
- EXAMPLE:
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 2010-02-18 03:24 ata-Hitachi_HDS722020ALA330_JK1131YAGDU37V -> ../../sda lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 2010-02-18 03:24 ata-Hitachi_HDS722020ALA330_JK1131YAGDU37V-part1 -> ../../sda1 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 2010-02-18 03:24 ata-ST31000528AS_6VP08W65 -> ../../sdb
TIP: IDE/SATA hard drives will start with ata- and USB hard drives will start with usb-.
Partition/Format
Compare the difference between before.txt and after.txt to determine the new hard drive(s) device name. This can be done automatically by executing:
diff before.txt after.txt
- EXAMPLE:
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 2010-02-18 03:24 ata-ST31000528AS_6VP08W65 -> ../../sdb
At this point, partition and format the hard drive(s) if they are new. For hard drive(s) that contain data to be preserved, skip to the Mount step.
Command-line (Fedora)
To partition the hard drive(s), execute the applicable commands (substitute sdX with hard drive device name, such as sdb):
parted /dev/sdX
- Up to 2TB, at the (parted) prompt, enter:
- mklabel (answer yes when prompted)
- mkpart primary 0% 100%
- quit
- Greater than 2TB, at the (parted) prompt, enter:
- mklabel gpt (answer yes when prompted)
- mkpart primary 0% 100%
- quit
Verify the new partition was created:
ls -l /dev/disk/by-uuid/
- EXAMPLE:
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Dec 29 18:10 1b8597e0-5d95-4474-b093-53099c8c81c9 -> ../../sda1
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Dec 29 18:10 1c161033-c695-4291-aba1-257d3987edf7 -> ../../dm-0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Dec 29 18:10 b7017251-cb54-438b-92a3-781537c565e6 -> ../../sdb
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Dec 29 18:10 c1fe62b3-41dc-4a67-8a6b-09f90b7893ba -> ../../dm-1
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Dec 29 18:10 e0f5a9bd-f52b-431e-89af-61da70659bdd -> ../../dm-2
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Dec 29 18:10 547b073d-e591-4913-b4fb-7c5084353979 -> ../../sdb1
The new partition is named sdX1 (i.e. sdb1 in RED).
Format the partition, execute (can substitute ext3):
mkfs.ext4 -j /dev/sdX1
Repeat the Partition/Format step for each hard drive to be partitioned and formatted.
GParted (Ubuntu)
From the HDA desktop (or using VNC), In a terminal as root and type gparted to launch the application.
Here's a general introduction on YouTube. Just use ext3 or ext4 instead of fat32 if you follow that tutorial.
For drives > 2.0 TB, following these steps:
- Choose hard disk in the dropdown menu (top right)
- Select Device > Create Partition Table... > Advanced > (Choose 'gpt')
- Create partition
- NOTE: GParted supports GUID-partitioned drives, however, the hda-mount script do not support currently.
Repeat the Partition/Format step for each hard drive to be partitioned and formatted.
Mount
Mount the hard drive(s)/partition(s) for use in the HDA.
Execute the following command. It will create drive1, drive2, etc and mount the hard drive(s) automatically:
hda-diskmount
- EXAMPLE:
**************************************************************** Ignoring /dev/sda1 - already in /etc/fstab or mounted **************************************************************** Mounted /dev/sdb1 as '/var/hda/files/drives/drive1' (read-write) You may want your system to mount it every time you boot. To do so, add this line VERY CAREFULLY to /etc/fstab and reboot: UUID=547b073d-e591-4913-b4fb-7c5084353979 /var/hda/files/drives/drive1 ext4 defaults 1 2 **************************************************************** All Linux, Windows and Mac partitions on non-removable disks have been mounted
The new hard drive storage space can be used for All Shares, Some Shares, or the Greyhole Storage Pool. Follow the guidance below based on desired usage.
Host ALL shares on the new hard drive.
Move all the shares data to the new drive by executing the following command (replace path in RED with the path from the hda-diskmount output line in BLUE):
mv /var/hda/files/* /var/hda/files/drives/drive1/
- NOTE: There may be a WARNING indicating /var/hda/files/drives cannot be moved to a subdirectory of itself which should be ignored.
Unmount the new hard drive:
umount /var/hda/files/drives/drive1/
Mount the new hard drive permanently as /var/hda/files, using the nano command line editor:
nano /etc/fstab
Add the line to /etc/fstab provided in the hda-diskmount output in BLUE and change the second value (path) to /var/hda/files.
- EXAMPLE hda-diskmount output (Original):
UUID=547b073d-e591-4913-b4fb-7c5084353979 /var/hda/files/drives/drive1 ext4 defaults 1 2
- EXAMPLE hda-diskmount output (Modified):
UUID=547b073d-e591-4913-b4fb-7c5084353979 /var/hda/files ext4 defaults 1 2
- EXAMPLE /etc/fstab:
#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Sat Nov 9 01:46:39 2013
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
UUID=1ebbf241-528c-465e-889f-acc15400dd8c / ext4 defaults 1 1
UUID=087b15a5-c3ca-4615-b6ee-bf5f399a803e /boot ext4 defaults 1 2
UUID=75346b8e-b162-458c-b0e9-a8d48ec2bc82 swap swap defaults 0 0
UUID=ad85eeb9-18f0-4b85-9bfa-b88a5d1489b3 swap swap defaults 0 0
UUID=547b073d-e591-4913-b4fb-7c5084353979 /var/hda/files ext4 defaults 1 2
Finally, execute the following:
mount -a ls /var/hda/files/
The last command will display contents of the new hard drive. All shares are now located on the new hard drive.
If you want only some of your shares to be on your new hard drive, here's how to do that.
First, you'll want to move your previous shares data, if any, into your new drive.
You only need to do this next command if you have data that you care about in the /var/hda/files/* folders (that you want on the new drive).
In a Terminal, as root, type the following command. Replace the path in red with the path you received when you ran hda-diskmount. Replace something with the name of the share you want to have on your new drive (the share should already exist).
mv /var/hda/files/something /var/hda/files/drives/drive1/
Repeat with every share you want on your new drive.
Next, you'll need to make the mount permanent
umount /var/hda/files/drives/drive1
nano /etc/fstab
In nano, you'll need to add a new line at the bottom. Take the line that hda-diskmount gave you, and insert that.
So, following previous examples, I should add this:
UUID=9d972abc-1639-44df-a60e-668618d40236 /var/hda/files/drives/drive1 ext4 defaults 1 2
Save and exit nano (CTRL-X, Y, ENTER), and try your new mount:
mount -a ls /var/hda/files/drives/drive1
That last command should show you the content of you new hard drive.
Now, you need to update the location of the moved shares within Amahi. Go to your Amahi Dashboard, click on Setup, then Shares.
Click on one of the shares that you have moved. This will open a panel revealing the share settings. Click on the location (the bit that is shown with a dotted underline) and it will change to an edit box. Update the location to match the new share location.
For example, the original movies location was: /var/hda/files/movies
The new location might be: /var/hda/files/drives/drive1/movies
Repeat for any other shares that you have moved. Check that you can access these shares from another machine within your network.
Finally, if you have any services that depend on the location of these shares, make sure they are configured to use the new share location. For example, if you have a DLNA server installed, check its configuration files to make sure that it can find any media folders that have been moved. Secondly, check that all such services start correctly and behave as expected. If the service doesn't start, it may be that it is testing for a specific location during the service startup. Check the startup files in /etc/init.d to see if this is the case.
That's it. Your share(s) are now on your new hard drive.
Greyhole Storage Pool
USe new hard drive for Greyhole Storage Pool.
In a Terminal, as root, edit /etc/fstab:
nano /etc/fstab
- EXAMPLE:
#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Sat Nov 9 01:46:39 2013
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
UUID=1ebbf241-528c-465e-889f-acc15400dd8c / ext4 defaults 1 1
UUID=087b15a5-c3ca-4615-b6ee-bf5f399a803e /boot ext4 defaults 1 2
UUID=75346b8e-b162-458c-b0e9-a8d48ec2bc82 swap swap defaults 0 0
UUID=ad85eeb9-18f0-4b85-9bfa-b88a5d1489b3 swap swap defaults 0 0
UUID=547b073d-e591-4913-b4fb-7c5084353979 /var/hda/files/drives/drive1 ext4 defaults 1 2
The line in BLUE is what you need to copy and add to the bottom of /etc/fstab. This is REQUIRED for the hard drive(s) to be permanently mounted.
There will be multiple lines for multiple hard drive(s) added. Ensure you copy and add ONLY those which were not present in the before.txt file.
Verify the hard drive(s)/partition(s) configuration is correct in /etc/fstab.
Refer to Greyhole (Amahi 6) for Ubuntu or Greyhole (Amahi 7) for Fedora to configure the Greyhole Storage Pool.
Verify/Test
Verify the hard drive/partition is mounted:
df -h
- EXAMPLE:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/sda5 16G 4.3G 11G 30% / devtmpfs 493M 0 493M 0% /dev tmpfs 498M 84K 498M 1% /dev/shm tmpfs 498M 364K 498M 1% /run tmpfs 498M 0 498M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup tmpfs 498M 1.1M 497M 1% /tmp /dev/sda1 190M 75M 102M 43% /boot /dev/sdb1 917G 398G 473G 46% /var/hda/files/drives/drive1
The hard drive(s) and the mount point (path) should be listed for each hard drive added. If not, then further investigation will be needed to determine the problem.
Tips
Mount Order
The following will outline how to manually order your disks and mount drives automatically on boot.
1. First, get the UUID for each drive by opening a terminal and entering command
gstreet@gstreet-MicroServer:~$ sudo blkid [sudo] password for gstreet: /dev/sda1: LABEL="Seagate-Alpha2TB" UUID="55d9333f-d801-425a-b2af-d65c5966d56f" TYPE="ext4" /dev/sdb1: LABEL="Seagate-Beta2TB" UUID="5bd5498f-30c1-4780-948e-ca46656507d2" TYPE="ext4" /dev/sdc1: LABEL="WD-Charlie2TB" UUID="a7337504-376a-4d36-9f7a-1a24c0f55fbd" TYPE="ext4" /dev/sdd1: LABEL="WD-Delta2TB" UUID="8d881dcb-8de3-4621-b9bd-00025196868a" TYPE="ext4" /dev/sde1: LABEL="root" UUID="4d6f8004-d190-4234-a03b-b68de988abf0" TYPE="ext4" /dev/sde3: LABEL="home" UUID="d0531fa1-9311-4d53-b838-f35898adbd98" TYPE="ext4" /dev/sde5: LABEL="swap" UUID="3c39206c-ba60-47ff-a1fe-f5821b2ab543" TYPE="swap"
In this case, the user has four data drives (sda1, sdb1, sdc1, sdd1) and the Operating system assigned to a fifth drive, sde.
Take note of the UUID's for each drive. Easiest to cut and paste UUID's straight from the terminal - no typo's!
2. Then edit /etc/fstab to mount each drive - for novices, easiest to do this using a graphical editor. You might consider first making a copy called fstab.bak (use the "save as" command, close file and then gedit the original fstab again) so that you can recover the original fstab file if you make mistakes.
sudo nano /etc/fstab
3. Then very carefully add the following line for each disk into the end of the fstab file. Make sure you paste in the right UUID, drive number and drive file system (ext4 in this case).
UUID=55d9333f-d801-425a-b2af-d65c5966d56f /var/hda/files/drives/drive1 ext4 defaults 1 2
It should look something like the following when lines are added for each of the five drives in this example. Note lines beginning with # are comments where the remainder of the line is ignored)
# Mounting Greyhole Drives for Drive Pool. # # Drive1 = Seagate-Alpha2TB in Microserver Bay 1 from left UUID=55d9333f-d801-425a-b2af-d65c5966d56f /var/hda/files/drives/drive1 ext4 defaults 1 2 # # Drive2 = Seagate-Beta2TB in Microserver Bay 2 from left UUID=5bd5498f-30c1-4780-948e-ca46656507d2 /var/hda/files/drives/drive2 ext4 defaults 1 2 # # Drive3 = WD-Charlie2TB in Microserver Bay 3 from left UUID=a7337504-376a-4d36-9f7a-1a24c0f55fbd /var/hda/files/drives/drive3 ext4 defaults 1 2 # # Drive4 = WD-Delta2TB in Microserver Bay 4 from left UUID=8d881dcb-8de3-4621-b9bd-00025196868a /var/hda/files/drives/drive4 ext4 defaults 1 2 # # Drive5 = 250GB OS Drive mounted in Optical Drive bay UUID="4d6f8004-d190-4234-a03b-b68de988abf0 /var/hda/files/drives/drive5 ext4 defaults 1 2 # #
Save the file and quit the editor. To see if that will work at boot time, try with:
mount -a
If that gives you errors, there is a good chance that this line was not added properly and your machine may not reboot and get stuck mounting the drives!
Note that the hda-diskmount command had already added lines to mount my OS drive which had two partitions (root or /, and home). Save file and close.
4. Save file and reboot machine.
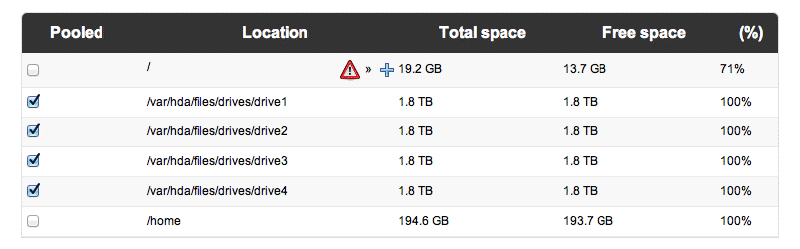
5. Check that drives have successfully mounted in Amahi hda (Setup - Shares - Storage Pool)
In this case, if all drives mounted successfully, it should look like (Ubuntu):
Bad Blocks
Optionally, you can test your new drive for bad blocks.
- NOTE: This can take a long time to complete! Recommend starting it in the evening so it will be completed the next day.
In a Terminal, as root, type the following command. Replace sdb1 with the (green) value you received from hda-diskmount.
e2fsck -cn /dev/sdb1
You'll receive a warning that says "WARNING!!! Running e2fsck on a mounted filesystem may cause SEVERE filesystem damage. Do you really want to continue (y/n)?"
Answer yes. The -cn option we're using can safely be used on mounted filesystems.
Troubleshooting
If hda-diskmount does not mount the hard drive, you can manually do it.
Complete the following steps:
- Create the mount point (choose one NOT in use)
mkdir -p /var/hda/files/drives/drive1
- Identify the hard drive to mount and copy the UUID from the output that corresponds to the hard drive (i.e. sdb)
ls -l /dev/disk/by-uuid/
- EXAMPLE:
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Dec 29 18:10 1b8597e0-5d95-4474-b093-53099c8c81c9 -> ../../sda1
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Dec 29 18:10 1c161033-c695-4291-aba1-257d3987edf7 -> ../../dm-0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Dec 29 18:10 b7017251-cb54-438b-92a3-781537c565e6 -> ../../sdb
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Dec 29 18:10 c1fe62b3-41dc-4a67-8a6b-09f90b7893ba -> ../../dm-1
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Dec 29 18:10 e0f5a9bd-f52b-431e-89af-61da70659bdd -> ../../dm-2
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Dec 29 18:10 547b073d-e591-4913-b4fb-7c5084353979 -> ../../sdb1
- The UUID for sdX1 (i.e. sdb1 is RED).
- Add the following to the end of /etc/fstab, replacing the UUID as captured in the previous step
nano /etc/fstab
- EXAMPLE:
#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Sat Nov 9 01:46:39 2013
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
UUID=1ebbf241-528c-465e-889f-acc15400dd8c / ext4 defaults 1 1
UUID=087b15a5-c3ca-4615-b6ee-bf5f399a803e /boot ext4 defaults 1 2
UUID=75346b8e-b162-458c-b0e9-a8d48ec2bc82 swap swap defaults 0 0
UUID=ad85eeb9-18f0-4b85-9bfa-b88a5d1489b3 swap swap defaults 0 0
UUID=547b073d-e591-4913-b4fb-7c5084353979 /var/hda/files/drives/drive1 ext4 defaults 1 2
- The new entry will be mounted as /var/hda/files/drives/drive1 (i.e. sdb1 in BLUE)
- Mount the hard drive
mount -a
- If all goes well, there should not be any output. If there are errors, stop and diagnose the problem.
- Accomplish Verify/Test step to ensure the hard drive is properly mounted.
Repeat this process for each hard drive to be mounted.
Help
If you need assistance, please post in the Amahi Forums or receive LIVE support on the Amahi IRC channel.