Difference between revisions of "Greyhole"
| Line 146: | Line 146: | ||
'''Amahi application to view the Greyhole log in your web browser:''' [http://www.amahi.org/apps/greyhole-logmon Greyhole LogMon] | '''Amahi application to view the Greyhole log in your web browser:''' [http://www.amahi.org/apps/greyhole-logmon Greyhole LogMon] | ||
| − | == Convert Greyhole from SQLite to MySQL == | + | <!--== Convert Greyhole from SQLite to MySQL == |
Greyhole is already using MySQL in Amahi 6.0 | Greyhole is already using MySQL in Amahi 6.0 | ||
| Line 160: | Line 160: | ||
grep db_engine /etc/greyhole.conf | grep db_engine /etc/greyhole.conf | ||
| + | --> | ||
== Disable Greyhole == | == Disable Greyhole == | ||
Revision as of 03:51, 5 April 2014
Contents
- 1 What is Greyhole
- 2 Important Warnings
- 3 Forcing an fsck
- 4 First things first
- 5 For Storage Pool (Ubuntu)
- 6 Greyhole Options (Ubuntu)
- 7 Greyhole Advanced Options
- 8 Copying data to shares for the first time
- 9 Adding a new drive to your HDA and storage pool
- 10 Drive Mounted as /media
- 11 Monitoring Greyhole
- 12 Disable Greyhole
- 13 Testing and Reliability
- 14 Reconnect the Greyhole storage pool
- 15 Greyhole Troubleshooting
- 16 Landing Zone Considerations
- 17 Manually updating Greyhole for Amahi
- 18 Emptying Greyhole Attic
- 19 Moving drives/data out of Greyhole
- 20 Changing Greyhole drive mount points
- 21 Reference
What is Greyhole
Greyhole is Amahi's Storage pooling technology. Storage Pooling combines the space of multiple disk drives and makes them look as if they were all part of a single pool of disk space. Specifically, Greyhole:
- Combines the space from multiple drives into a single volume
- Distributes files across all drives in the pool
- Creates multiple copies of files in admin-specified shares
This feature is installed by default, but requires a few simple steps to begin utilizing the features.
You can add additional drives to your hda and prepare them for use in Greyhole by following this tutorial.
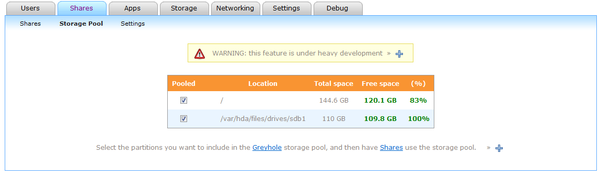
To add a drive to your Greyhole storage pool. Open your HDA dashboard and navigate to the Shares tab. Then click on the Storage Pool sub-category. You will see a page similar to the one below.
Important Warnings
You should be safe reading existing files directly, or adding new files directly, as long as don't care that your new files will only be moved into the storage pool during the next check, which runs automatically at midnight (or manually using greyhole --fsck). Until then, your new files will be stored in your shared directories (normally /var/hda/files/share_name/).
Also, touching anything inside the gh directories that Greyhole creates at the root of your partitions is a recipe for disaster. We strongly discourage you from using the root partition in a drive pool.
NOTE: All commands are executed as root user (Fedora) or preceded with sudo (Ubuntu).
Forcing an fsck
greyhole -fsck greyhole -f
will run an fsck ONLY if the greyhole or samba configurations have changed.
greyhole --fsck
will force a fsck.
First things first
You need to go in the Settings tab, and enable Enable Advanced Settings. Without Advanced Settings enabled, you won't see the following page and options.
NOTE: Amahi 7 currently does not include Greyhole configuration integrated with the dashboard. See Greyhole Configuration for details.
For Storage Pool (Ubuntu)
Select the drives you want available for your storage pool.
Greyhole Options (Ubuntu)
The next step is to select the share you want to replicate across the pool.
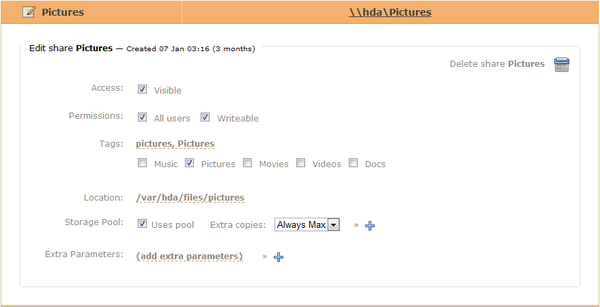
From the Shares tab, select the Shares sub-catagory. We chose the Pictures share for this tutorial.
Check the option for "Uses pool" and choose the number of drives to replicate this share. In this instance we have chosen to use all drives available to the greyhole pool.
Note: Greyhole is not a backup solution. If a file is removed, all copies are removed.
Greyhole Advanced Options
You can further configure Greyhole by manually editing /var/hda/platform/html/config/greyhole.yml.
To see what options are available, and what they do, refer to the sample greyhole.conf provided with Greyhole.
greyhole.yml is in in YAML format. Most of it should be easy enough to modify. The only exception would be the sticky_files (and optional sticky_into) options.
Here's an example of how those should appear:
To specify the following to Greyhole in greyhole.conf:
sticky_files = Music/
sticky_files = Videos/Movies/
stick_into = /mnt/hdd1/gh
stick_into = /mnt/hdd5/gh
sticky_files = Backups/CrashPlan/
stick_into = /mnt/hdd0/gh
one should specify this in the greyhole.yml file, where precise indentation matters:
sticky_files:
- - Music/
- - Videos/Movies/
- - /mnt/hdd1/gh
- /mnt/hdd5/gh
- - Backups/CrashPlan/
- - /mnt/hdd0/gh
For your changes to be effective, you'll need to force Amahi to regenerate the greyhole.conf file. You can do so by editing a share, clicking it's path, and just clicking the Save button without actually changing the path.
When you start using Greyhole, you might want to copy or move all your existing files into your new shares that use the storage pool.
Note: This is not necessary if your files are already in Amahi shares. If they are there, and you enable the Uses pool option in the Amahi dashboard, the files will start getting moved around into the drives in your storage pool during the night (starting at midnight), when the nightly storage pool check starts.
The instructions below are for users who have more data to copy into the Greyhole shares than their currently free space in the /var/hda/files/ folder.
One way to do that is to mount the shares that use the Greyhole storage pool, either on the HDA itself, or on a client computer on your local network, and copy your data from their existing location into the mounted shares. This can be time consuming, but it is the safest way to use Greyhole.
Another way to move your files from their current location into the storage pool is to share their current location using an Amahi share that Uses pool, then let Greyhole's nightly check move the files from there into the pool.
Here's a more detailed walkthrough for this method:
- Setup the Greyhole Storage Pool in the Amahi dashboard, Shares > Storage Pool page.
- Go in the Shares > Shares page. In there, make sure you have an existing share for each share you have data for. Create new ones if you need, remove the ones you don't need.
- Edit the path of each of those shares, and enter the current location of your existing data. For example, the Movies share could have a path = /media/External Drive/Movies
- Enable the Uses pool option for each of your shares, and select the number of extra copies you'd like, if any.
- Now, you either need to wait for Greyhole's nightly check to start, or you can start it manually from a terminal, as root, using this command: greyhole --fsck
- Monitor /var/log/greyhole.log to see when the fsck operation is done.
- Once fsck is done, your data has now been moved into the Greyhole storage pool (in the drives you selected in Shares > Storage Pool). All that should be left in the previous location of your data (/media/External Drive/Movies from the previous example) should be symbolic links pointing to the new file copies. If the previous location is just empty directories (no symlinks), do not panic. This is normal if your previous location is an NTFS or FAT partition (drive).
- Move all those directories / symlinks from there into the correct folders in /var/hda/files/share_name
- Back in the Amahi dashboard, edit the path of the shares once again, and put back /var/hda/files/share_name (i.e. the folders where you moved the symbolic links).
- If you used an NTFS or FAT partition for the previous location, you'll need another fsck to create the symlinks where they should be. Either wait for midnight, or launch it manually, from a command line, as root: greyhole --fsck
You're done. All your existing data is now stored in the various drives included in your storage pool, and are accessible via the Samba shares you have defined in the Amahi dashboard.
Adding a new drive to your HDA and storage pool
See Adding a new drive to your HDA and to your Greyhole storage pool.
Drive Mounted as /media
Including any drive mounted as /media/Something in your storage pool is usually a bad idea.
Those mounts are created by the gnome-automounter, which requires you to be logged in into X (Gnome) to become available.
This will create issues with Greyhole, which expects drives to always be available, and will take action when some of them are missing.
Follow this guide to permanently mount your drives, before you include them in your storage pool.
Monitoring Greyhole
Sometimes you might want to monitor what Greyhole is doing, for example when writing data to your greyhole shares for the first time. Here are a few commands you can type in a terminal to follow along.
Scrolling view of total Greyhole operations queue:
while [ 1 == 1 ]; do greyhole --view-queue | grep Total; sleep 60; done
Alternate way to watch Greyhole operations queue:
watch -d greyhole --view-queue
Scrolling log of what files Greyhole is working on right now:
tail -f /var/log/greyhole.log
Amahi application to view the Greyhole log in your web browser: Greyhole LogMon
Disable Greyhole
For those who do not use Greyhole, you can disable it. This is based on the fact you never have used it by enabling 'Uses pool' on any share. Recommend using extreme caution as this could have unpredictable results.
Perform the following steps as user root (Ubuntu):
update-rc.d -f greyhole remove rm /etc/monit.d/greyhole.conf service monit restart service greyhole stop
DO NOT attempt to remove the Greyhole package as it is a dependency of the HDA software. Doing so will break your HDA.
Testing and Reliability
Check out the Greyhole grinder to help make Greyhole rock solid.
Reconnect the Greyhole storage pool
If you upgrade and/or reinstall Amahi and need to get your drives with data on them to the new system, follow this Reconnect existing Greyhole storage pool guide.
Greyhole Troubleshooting
Landing Zone Considerations
The landing zone or LZ is the area where files arrive first before being distributed to their final destination. See details in the Greyhole landing zone page.
Manually updating Greyhole for Amahi
See Greyhole updating for Ubuntu ONLY.
Emptying Greyhole Attic
greyhole --empty-attic
About the attic: The attic is used like a Recycle Bin, or Trash. That means you'll need to manually empty it once in a while. To do so, use the --empty-attic parameter (see above). Another option is to create a 'Greyhole Attic' Samba share. More details about that here.
Moving drives/data out of Greyhole
You may need to remove a drive from Greyhole and transfer the share files to another drive: Greyhole moving data out of the pool
Changing Greyhole drive mount points
Refer to Changing Greyhole Mount Points.
Reference
- Good article on Greyhole with terms explained.
- Greyhole Wiki: Provides guidance for various tasks.